

If the choroidal nevus has one or more of these findings, it is labeled a suspicious choroidal nevus that has a chance of turning into or even being a small choroidal melanoma.Ī choroidal nevus can have yellow-white spots on its surface called drusen or drusenoid retinal pigment epithelial detachments (DRPED).These are signs of retinal dysfunction.
#BEAR TRACKS RETINA TREATMENT PROFESSIONAL#
Your eye care professional will look to see if the choroidal nevus is raised (has thickness), orange pigment (lipofuscin), or is leaking fluid (retinal detachment). A choroidal nevus is typically gray but can be brown, yellow or variably pigmented. Diagnosis This image demonstrates how a suspicious choroidal nevus can demonstrate focal leakage on fluorescein angiography.Ĭhoroidal nevus is typically a pigmented tumor of the blood vessel layer (choroid) beneath the retina. Such changes can cause a localized retinal detachment/degeneration, flashing lights and loss of vision.Ī typical choroidal nevus is asymptomatic or “causes no symptoms” and found by routine dilated eye examination with ophthalmoscopy. However, if a choroidal nevus leaks fluid or is associated with the growth of abnormal blood vessels (neovascularization) patients can become symptomatic. SymptomsĪ benign choroidal nevus (eye freckle) rarely causes symptoms. This picture can be compared to future examinations to help determine if the nevus has changed or stayed the same. It is a good idea for each patient to keep a picture of your choroidal nevus. This examination may include the use of ultrasound, specialized photography, optical coherence tomography or an intraocular angiogram. It is reasonable to have an eye cancer specialist check to see if your choroidal nevus looks suspicious and take baseline measurements. Such tumors should be followed most closely for evidence of growth or malignant transformation into a choroidal melanoma. If a choroidal nevus is leaking subretinal fluid, this is a particularly ominous sign. If the choroidal nevus has orange pigment or has thickened, it should be checked more often. Only your doctor can look inside your eye to see if the choroidal nevus has changed. If the choroidal nevus has orange pigmentation, if the nevus is leaking fluid, or has a thickness of 2 mm or more it may be (or become) a malignant choroidal melanoma.ĭepending on its appearance, patients with a choroidal nevus should have their eyes examined (at least) every 6 months. Photography is typically used to document the size of the choroidal nevus. Like a nevus on the skin, a choroidal nevus can grow into a malignant melanoma.Ī choroidal nevus rarely requires treatment. The most common “choroidal nevus” or eye nevus are unusual and can only be seen by an eye care specialist. Like a raised freckle on the skin, nevi can also occur inside your eye. Finger, MD Description A benign appearing choroidal nevus (eye freckle). CHRPE block choroidal fluorescence on fluorescein angiography.By Paul T. CHRPE that are associated with FAP are described as atypical, being oval or even fishtail-like in shape, bilateral, more isolated in position rather than grouped together and variable in size up to approximately a disc diameter. The multifocal, so-called bear-track form of CHRPE is often confined to a specific area within the fundus. Some CHRPEs are conspicuously lacking in pigment, just having a pigmented edge. This is sometimes referred to as a sunburst effect. Further depigmented areas or lacunae may develop within the lesion with time. Frequently, a depigmented halo lies just inside the edge of the lesion.
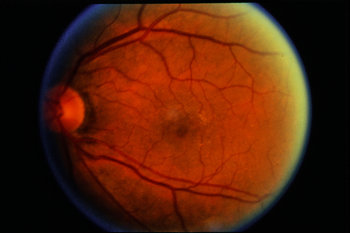
They can range from very small to many disc diameters in size. There are no symptoms associated with CHRPE.Ī typical CHRPE is flat and black or grey, with a sharply defined border, contrasting with the slate-grey, ill-defined appearance of a choroidal naevus. Congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE - 'chirpy') is a benign condition where the pigmentary lesions may be unilateral or bilateral, solitary or multifocal, with the latter sometimes being in the form of smaller patches that are grouped together, giving the impression of animal paw-prints (bear tracks) in the fundus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
